In a beef herd, profitability is determined by several factors, including the total weight of calves sold, cost of maintaining the cow herd, percentage of cows bred that wean a calf, and the price received for calves. The most critical times to influence these factors are the two months prior to calving and through breeding. A cow’s nutrition during this critical stage of production also has a direct impact on the ability of the cow to rebreed in a timely manner.
Failure to manage the nutrition of the cow herd during these critical times can hurt productivity, and profitability. Supplementing the herd with important vitamins, minerals and proteins before calving and through breeding has been research-proven to improve a cow’s body condition and conception rates and, in turn, overall calf health and survival rates, making this an important time for supplementation.
“Research by the University of Nebraska with heifer offspring from cows grazing a dormant range, showed that in areas where protein was deficient in the forage, protein supplementation to the pregnant cow in late gestation resulted in heifer offspring that were heavier at weaning, pre-breeding, first pregnancy diagnosis, and before their second breeding season, as well as had greater pregnancy rates and calving 21 days earlier than heifers from non-protein supplemented cows,” said Kevin Glaubius, BioZyme® Director of Nutrition and Technical Sales. “These recent studies clearly show that there are areas where many beef producers lose productivity in the normal production settings that are never measured.”
It is important to make sure feed rations are formulated to meet or exceed the nutritional requirements of the cow during early gestation (roughly the first 60 days). While the particular vitamins and minerals fed during this time are very important, BioZyme stresses to its customers that it is also imperative to ensure that the proper amounts of energy and protein are supplied. These are needed to meet the increased demands during lactation and subsequent breeding.
Energy is probably the most important nutritional consideration in beef cattle production. Cows need energy to maintain milk production and to initiate and maintain pregnancy. Energy requirements increase significantly during the last third of pregnancy and while the cow is producing milk. Protein is the second limiting nutrient in most rations. Without adequate amounts of protein in the diet, daily feed consumption drops off, feed passage rates decrease and overall digestive efficiency declines.
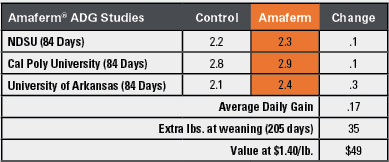
Research has proven that feeding Amaferm, found in BioZyme’s highly fortified Concept•Aid product line, can increase energy production by 16% and microbial protein by 34%. In addition, Concept•Aid is formulated at 250% of nutritional requirements to ensure the highest producing 25% of the cowherd is not nutritionally challenged. Concept•Aid contains proteinated copper, zinc and manganese to ensure maximum availability to the animal.
Mineral supplementation may not replace all of a cow’s winter supplement needs, however, it will reduce energy and protein supplementation costs and the average number of days from calving to rebreeding. Supplementation should increase profit potential, increasing the total pounds of calves weaned and leave producers more time to focus on their breeding strategies.